Looking at this year’s never-ending hacks, one wonders why they happen so frequently. Have audit firms actually gotten worse at what they do?
This, in my opinion, is not the case; yet, the topic is rather tricky because you can, in certain ways, reduce the risks to yourself and your project!
The need for robust security tooling is becoming increasingly critical as the attacks are becoming more complicated and coming from different directions apart from code. One innovative solution that is on the front-line in addressing these challenges is Guardrail, a real-time web3 security monitoring platform designed to catch bugs and potential threats before they become deadly, via advanced context-driven monitoring mechanisms.
Audits & Bug-Bounty
Hacks like the one that occurred lately occur as a result of organizations running too many upgrades… There are too many! Contracts should always be redeployed, fixed, and updated. Auditor work is much slower and takes more time.
To mitigate these risks, developers and projects turn to two crucial practices: bug bounties and audits. In this article, we will explore the importance of bug bounty programs and smart contract audits, highlighting their essential role in ensuring the integrity and security of Web3 systems!
Moreover, auditing a smart contract before (and, of course, after!) the launch of a project is of utmost importance. Smart contracts operate based on a predefined set of rules and conditions. Thereby, any error or logical flaw in the code can result in unexpected behavior or vulnerabilities that can be exploited!
Auditors and bug-bounty hunters typically examine the smart contract for any logical flaws (they just do it differently!), inconsistencies in business logic, or unintended consequences of specific contract actions. By identifying and rectifying logic errors during the auditing process, we can ensure that the smart contract functions exactly as intended before it is deployed.
By investing time and resources into a thorough assessment, developers can identify and rectify potential issues, thereby minimizing the chance of financial loss, reputation damage, or legal non-compliance. Audits & bug-bounty not only protect the project and its users but also contributes to the overall growth and adoption of the Web3 ecosystem!
Six Stages of Securing Your Smart Contract — by Orb
-
Research: what infrastructure to use, discuss how to design and correctly implement the smart contracts, and document;
-
Develop: Developers implement research and write the system’s code;
-
Test: Testing software to find bugs, problems, and improvement areas;
-
Deploy: Deploying software onto main-net for production;
-
Monitor: Developers evaluate and modify the system to ensure it performs its intended functions;
-
Incident Response: The acting stage involves monitoring and reacting to a bug report or an ongoing exploit.
Having these different stages allows you to approach the security of your smart contracts effectively while also focusing on other parts of the building process.
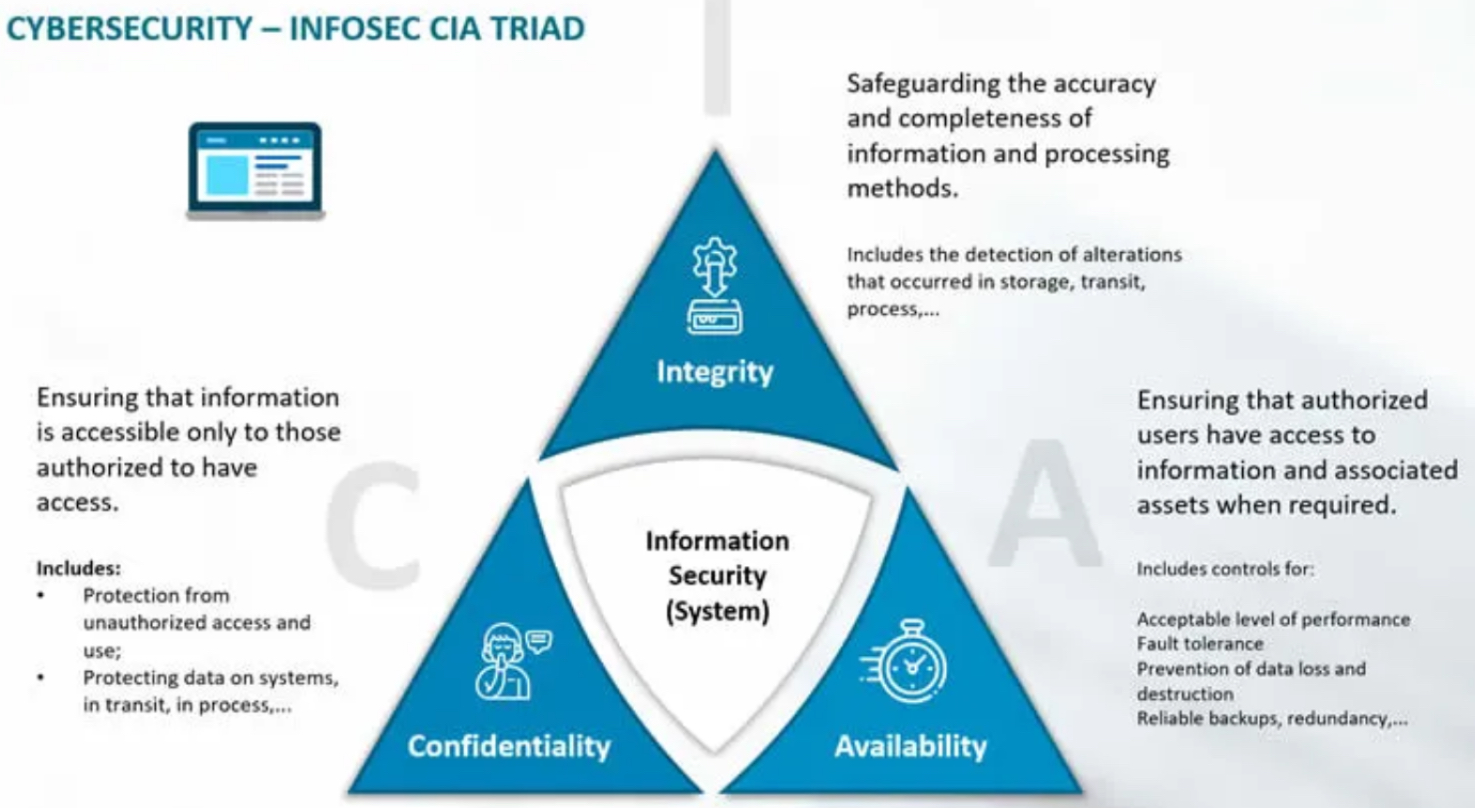
Image Source | What is the CIA Triad and Why is it important? | The opposites of the CIA Triad is DAD | More information!
Overall, Web3 represents a paradigm shift in the way we think about the internet. By prioritizing decentralization, trust, and user empowerment, it aims to create a more open, inclusive, and equitable digital ecosystem that aligns with the original vision of the internet. In my opinion, we must follow the same paradigm in our approach to Web3 security!
Emerging Threats in Crypto
Companies in this situation are pursuing the number of people and introducing upgrades faster than they have time to check, and it’s unexpectedly not their fault — after all, they do business and are quite confident in what they do.
At the same time, many projects discover about the occurrence after it has occurred, when there is almost nothing they can do and can only try to comfort their own community, which will have no effect unless serious action is taken to protect the project.
To begin, blockchain is a different layer, which we will refer to as the data-layer for convenience, and it is in line with the front-end and back-end, so we must organize a separate monitoring. This is critical to do, first and foremost to grasp how blockchain works and what types of assaults exist — in NFT, Meta-verse, DeFi, DEX, and so on.
You will be able to set up the appropriate alerts and active protection based on this data, for example, knowing which specific changes of your smart contract are especially important to watch.
But how? Let’s turn to the father of all blockchains — banking compliance system and banking security, after all, it is their replacement in each individual case by a few DApp and we all consider as the signs of that very mass adoption of the smart contracts.
If we finally want to give people the opportunity to be their own bank, we must realize that in this case people must be able to replace all those services and actions for which traditional banks get money!
So, as a rule, in such serious institutions as banks, local security services use such things as DLP and SIEM. In the same way, organizations can use different security technologies for detection of insider threats. You can also think of on-chain monitoring like a security camera for your smart contract that can catch threats in-real time as we can try to visualize this.
Data loss prevention software detects potential data breaches/data ex-filtration transmissions and prevents them by monitoring, detecting and blocking sensitive data while in use, in motion, and at rest. The terms “data loss” and “data leak” are related and are often used interchangeably.
For example, DLP encryption protocols can inform the organizations when a large file gets missing from the server. Likewise, the SIEM solutions can detect and inform you about insider threats if detected.
Security information and event management is a field within the field of computer security, where software products and services combine security information management and security event management. They provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware.
So let’s focus on that in a bit more detail in the prism of the blockchain-based smart contracts. In blockchain we are dealing with not quite normal characteristics and with a lot of data at the same time, but all the things I listed above can be done at the blockchain level as well.
For example, here is the technology I described in late 2020, and it is similar to the implementation of roughly the same web2-origin thing but in blockchain:
Onchain Monitoring
Imagine the situation , you are the owner or employee of a large DeFi protocol based on smart contracts, and hundreds of people start tweeting to you and you realize with horror that their anger is justified because your project was hacked and right now they are taking money out of it, using the Reentrancy attack.
Most likely, you will make a lot of mistakes and will not immediately understand what to do. But what would happen if you had monitoring installed?
Your technical team could have been notified of the attack during the preparation stage itself (when the money started flowing out of the system).To do this, monitoring should not only work for notification. And the best would be if they will duplicate each other, and common events will be managed by the “head” program acting like a classic SIEM.
Does that sound cool? It is, because you can combine all three principles of reliable protection — prevention, internal response to minimize damage from an attack, and active protection against the actions of a hacker!
Can proactive security solutions like real-time monitoring be combined with circuit breakers effectively?
Circuit breakers in smart contracts aren’t just code features — they’re monitoring systems that detect anomalies and trigger protective responses in real-time.
While ERC-7265 standardizes on-chain circuit breakers, the real innovation lies in intelligent monitoring that acts as an external circuit breaker to help prevent billions in losses before they happen.
Layer 1: Onchain circuit breakers
These are the standardized mechanisms built into smart contracts themselves, like the proposed ERC-7265 standard.
ERC-7265 circuit breaker mechanics:
-
Threshold-based triggers: Halt outflows when withdrawals exceed predefined limits;
-
Customizable responses: Either revert transactions or delay settlement;
-
Protocol-agnostic design: Works across different DeFi protocols.
Example Implementation:
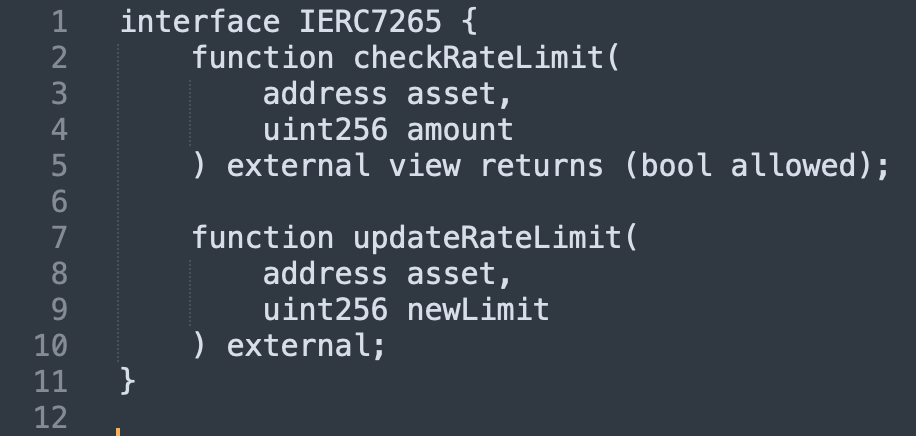
The Limitation: on-chain circuit breakers are reactive — they respond after anomalous behavior has already begun.
Layer 2: Real-time monitoring as circuit breakers
This is where the real innovation happens. Monitoring systems act as external circuit breakers by:
-
Detecting patterns before they become problems;
-
Triggering alerts in seconds, not minutes;
-
Enabling proactive response before significant losses;
-
Providing context that on-chain mechanisms can’t.
By acting as a safety net, circuit breakers can prevent further damage during a security incident, allowing developers to investigate and resolve the issue without risking additional losses. This feature is particularly beneficial in the volatile environment of Web3, where rapid response times can make a significant difference in mitigating potential damage.
Flash loan attack detection:
-
Normal Pattern: Small borrows → Normal repayment
-
Attack Pattern: $100M+ borrow → Complex arbitrage → Partial repayment
-
Monitoring Response: Alert in 15 seconds → Manual review → Block if necessary
-
The Advantage: Catches attacks that stay within individual protocol limits but are clearly malicious when viewed holistically.
Smart contract circuit breakers are more than simply emergency pause buttons; they are all-in-one monitoring systems that instantly identify, assess, and react to hazards. The true innovation is intelligent monitoring that serves as an external circuit breaker, even as ERC-7265 standardizes onchain protections.
By acting as a safety net, circuit breakers can prevent further damage during a security incident, allowing developers to investigate and resolve the issue without risking additional losses. This feature is particularly beneficial in the volatile environment of Web3, where rapid response times can make a significant difference in mitigating potential damage.
How Guardrail is helping secure protocols & why one should use it?
Guardrail’s real-time web3 monitoring uses cutting-edge technologies to defend decentralized apps against vulnerabilities, hacks, and exploits that could jeopardize user assets and data integrity. By taking a proactive stance, the likelihood of serious security breaches is reduced and any suspicious activity is quickly found and dealt with.
For example - here's how Guardrail would detect a flash loan attack:
-
Normal baseline: Protocol sees 10-20 transactions per minute
-
Attack begins: 200 transactions hit in 3 seconds
-
Pattern recognition: Guardrail identifies flash loan signature
-
Alert triggered: Team receives notification with transaction details
-
Response: Manual review initiated, suspicious contracts blocked
Total time: 15 seconds from attack start to containment
Guardrail’s system learns that when a new address suddenly borrows $100M and executes 50 transactions in one block, it's likely an attack, not normal DeFi activity.
So, Guardrail can automatically detect possible threats and vulnerabilities in a Web3 project by using machine learning algorithms and sophisticated analytics. In addition to saving developers time, this automated threat detection (with a remarkably low number of false positives!) improves the application’s overall security posture by guaranteeing that vulnerabilities are fixed before they can be exploited.
Web3 projects can greatly improve their overall security posture by incorporating Guardrail into their security framework. Circuit breakers, automated threat detection, and real-time monitoring work together to offer a complete defense against possible attacks, guaranteeing that applications stay safe and robust. Important to note that while audits catch bugs before deployment, they can't protect against attacks that happen after your code goes live. This is where real-time monitoring becomes essential...
It is impossible to overestimate the significance of security as the Web3 ecosystem expands. Guardrail provides a complete solution that tackles the particular difficulties encountered by decentralized applications, offering automated threat detection, real-time monitoring, and circuit breakers to improve security in general.
By adopting Guardrail, Web3 projects can not only protect their users and assets but also foster trust and confidence in their applications, paving the way for a more secure and resilient decentralized future. Their systems are capable of detecting threats in seconds and have prevented millions in potential losses via catching the attacker's footprint early and triggering timely alerts to the teams!
You can learn more about Guardrail here.